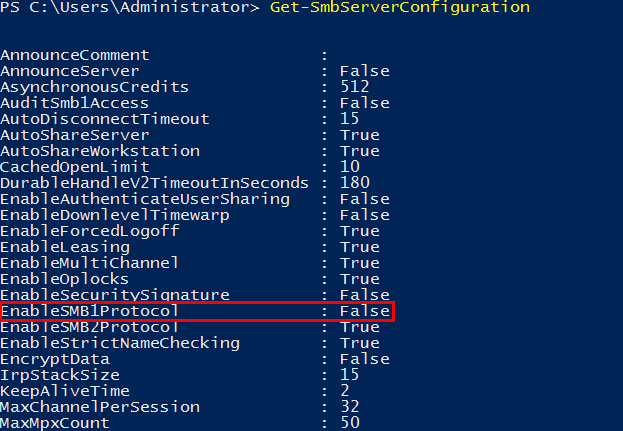
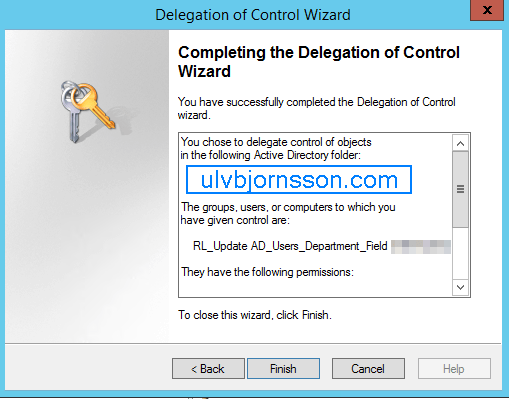
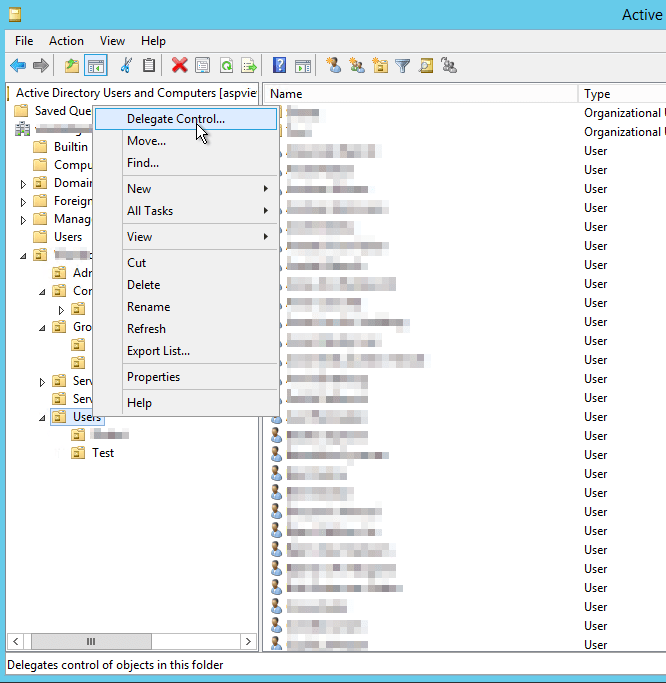
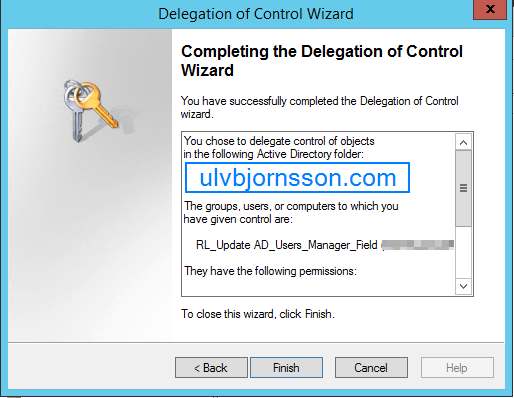
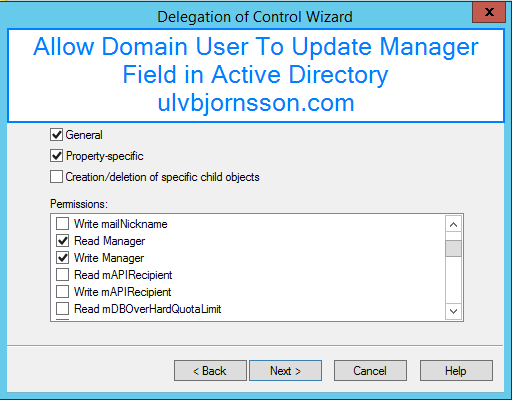
What is WannaCrypt?
- A large Ransomware campaign that spread across the world.
- The attack used a vulnerability that was patched in March 2017 Security Update (MS17-010, SMBv1)
- How can I mitigate WannaCrypt?
Timeline
August 2016
The Shadow Brokers attempt to auction NSA tools
- Claims they hacked Equation Group, author of Stuxnet and Flame
- Auction lists attack-ready code with 0-day exploits and trojans.
September 2016
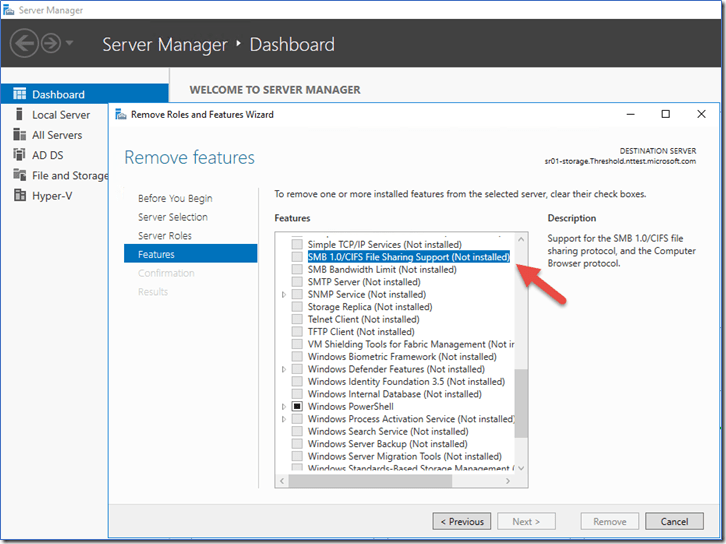
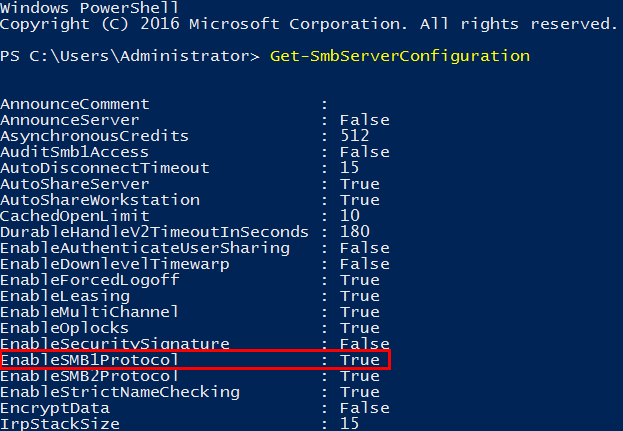
Microsoft encourages users to stop using SMB1
March 2017
Microsoft releases Security Update to address the MS17-010 for SMB1 vulnerability
April 2017
The Shadow Brokers release the toolbox
- Includes SMB (Eternal Blue) and the Trojan Code (Double Pulsar)
- Microsoft releases an advisory that no new vulnerabilities are found in Shadow Brokers release
May 2017
WannaCrypt is released by unknown attacker
Which utilizes [ETERNALBLUE] with [DOUBLE PULSAR] and a ransomware payload that demands 300-600 USD in Bitcoins from its infected hosts.
What does WannaCrypt do?
Infects
It attacks through [ETERNALBLUE] if MS17-010 is not installed.
Installs the Trojan if the attack is successful [DOUBLEPULSAR]
Encrypts
Encrypts 179 file types
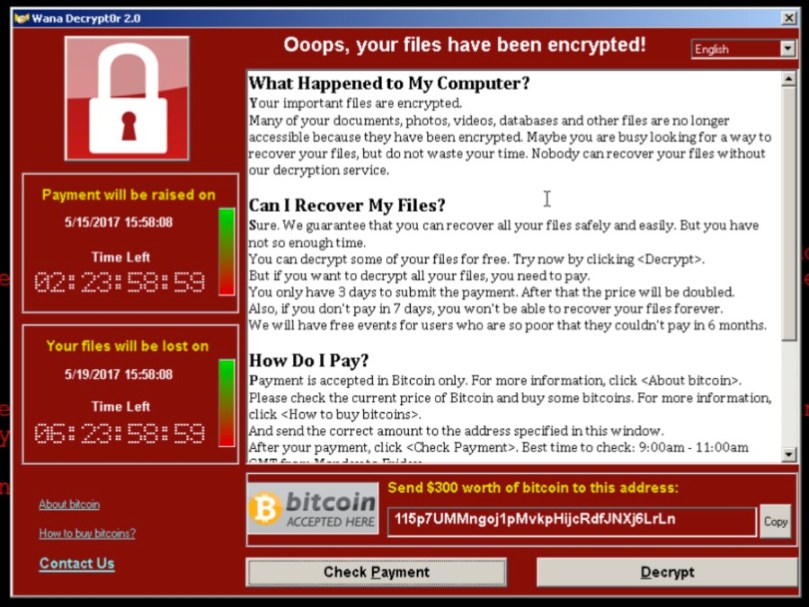
Shows a message that demands for payment of 300$-600$ in bitcoins to a listed wallet.
Spreads
It scans the local LAN and wider internet for port 445
Attempts to infect over SMBv1 [ETERNALBLUE] if port is open.
Payments
We find references to three different wallets these are:
115p7UMMngoj1pMvkpHijcRdfJNXj6LrLn 73 transactions, total of 17460 USD
13AM4VW2dhxYgXeQepoHkHSQuy6NgaEb94 98 transactions, total of 26570 USD
12t9YDPgwueZ9NyMgw519p7AA8isjr6SMw 82 transactions, total of 23450 USD
Which gives the attackers wallet a total of 67480 USD (14:00 GMT 16.05.17)
Curious of how to mitigate it, or want to read how to disable the SMBv1 vulnerability or patch it? Check out my previous article on mitigation.
As always, if you have suggestions on topics you want to read more about, or feedback. Leave a comment or tweet me at UlvBjornsson